Vue.js 技术揭秘之数据驱动
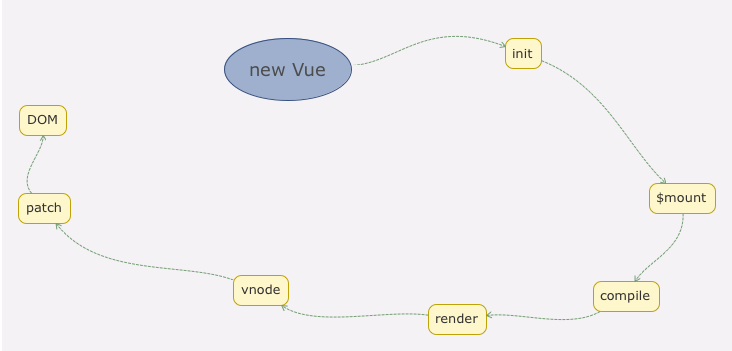
new Vue发生了什么
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
this._init(options)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) {
const vm: Component = this
...
// a flag to avoid this being observed
vm._isVue = true
// merge options
if (options && options._isComponent) {
// optimize internal component instantiation
// since dynamic options merging is pretty slow, and none of the
// internal component options needs special treatment.
initInternalComponent(vm, options)
} else {
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),
options || {},
vm
)
}
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
initProxy(vm)
} else {
vm._renderProxy = vm
}
// expose real self
vm._self = vm
initLifecycle(vm)
initEvents(vm)
initRender(vm)
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm)
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created')
...
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
vue的初始化
- 合并配置
- 初始化生命周期
- 初始化事件中心
- 初始化渲染
- 初始化data、props、computed、watcher等等
vue实例挂载的实现
$mount方法
- 缓存原型上的$mount方法
- 对传入的参数el做了限制,vue不能挂载到body,html这样的根节点上,
- 没有定义render方法,则会把则会把
el或者template字符串转换成render方法。 - vue是一个在线编译的过程,通过调用
compileToFunctions方法来实现 - 最后调用原型上的$mount 方法挂载
// 1
const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && query(el)
/* istanbul ignore if */
// 2
if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
`Do not mount Vue to <html> or <body> - mount to normal elements instead.`
)
return this
}
const options = this.$options
// resolve template/el and convert to render function
// 3
if (!options.render) {
let template = options.template
if (template) {
if (typeof template === 'string') {
if (template.charAt(0) === '#') {
template = idToTemplate(template)
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !template) {
warn(
`Template element not found or is empty: ${options.template}`,
this
)
}
}
} else if (template.nodeType) {
template = template.innerHTML
} else {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn('invalid template option:' + template, this)
}
return this
}
} else if (el) {
template = getOuterHTML(el)
}
if (template) {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
mark('compile')
}
const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(template, {
shouldDecodeNewlines,
shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref,
delimiters: options.delimiters,
comments: options.comments
}, this)
options.render = render
options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
mark('compile end')
measure(`vue ${this._name} compile`, 'compile', 'compile end')
}
}
}
return mount.call(this, el, hydrating)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
Vue.prototype.$mount
- el 它表示挂载的元素,可以是字符串,也可以是 DOM 对象
- 如果是字符串在浏览器环境下会调用
query方法转换成 DOM 对象的。 - 第二个参数是和服务端渲染相关,在浏览器环境下我们不需要传第二个参数
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined
return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
mountComponent
- 实例化一个渲染渲染
Watcher,- 初始化的时候执行回调函数
- 当vm实例中的监听数据发生变化的时候执行回调函数
- 在它的回调函数中会调用
updateComponent方法, - 在此方法中调用
vm._render方法先生成虚拟 Node,最终调用vm._update更新 DOM。
export function mountComponent (
vm: Component,
el: ?Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
vm.$el = el
if (!vm.$options.render) {
vm.$options.render = createEmptyVNode
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
// 编译环境下不符合规则的进行报警
}
}
callHook(vm, 'beforeMount')
let updateComponent
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
updateComponent = () => {
/*
相关逻辑代码 暂时不关心内部如何处理
*/
mark(startTag)
const vnode = vm._render()
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${name} render`, startTag, endTag)
mark(startTag)
vm._update(vnode, hydrating)
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${name} patch`, startTag, endTag)
}
} else {
updateComponent = () => {
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
}
}
// we set this to vm._watcher inside the watcher's constructor
// since the watcher's initial patch may call $forceUpdate (e.g. inside child
// component's mounted hook), which relies on vm._watcher being already defined
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {
before () {
if (vm._isMounted) {
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate')
}
}
}, true /* isRenderWatcher */)
hydrating = false
// manually mounted instance, call mounted on self
// mounted is called for render-created child components in its inserted hook
// vm.$vnode为null 表示当前是根vue的实例,
// 函数最后判断为根节点的时候设置 vm._isMounted 为 true, 表示这个实例已经挂载了,同时执行 mounted 钩 子函数
if (vm.$vnode == null) {
vm._isMounted = true
callHook(vm, 'mounted')
}
return vm
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
Vm._render()
Vue 的
_render方法是实例的一个私有方法,它用来把实例渲染成一个虚拟 Node
Vue.prototype._render = function (): VNode {
const vm: Component = this
const { render, _parentVnode } = vm.$options
// reset _rendered flag on slots for duplicate slot check
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
for (const key in vm.$slots) {
// $flow-disable-line
vm.$slots[key]._rendered = false
}
}
if (_parentVnode) {
vm.$scopedSlots = _parentVnode.data.scopedSlots || emptyObject
}
// set parent vnode. this allows render functions to have access
// to the data on the placeholder node.
vm.$vnode = _parentVnode
// render self
let vnode
try {
vnode = render.call(vm._renderProxy, vm.$createElement)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, vm, `render`)
// return error render result,
// or previous vnode to prevent render error causing blank component
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if (vm.$options.renderError) {
try {
vnode = vm.$options.renderError.call(vm._renderProxy, vm.$createElement, e)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, vm, `renderError`)
vnode = vm._vnode
}
} else {
vnode = vm._vnode
}
} else {
vnode = vm._vnode
}
}
// return empty vnode in case the render function errored out
if (!(vnode instanceof VNode)) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && Array.isArray(vnode)) {
warn(
'Multiple root nodes returned from render function. Render function ' +
'should return a single root node.',
vm
)
}
vnode = createEmptyVNode()
}
// set parent
vnode.parent = _parentVnode
return vnode
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
render方法的调用
render: function (createElement) {
return createElement('div', {
attrs: {
id: 'app'
},
}, this.message)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
总结:
vm._render 最终是通过执行 createElement 方法并返回的是 vnode,它是一个虚拟 Node
Virtual Dom
真正的dom元素是非常庞大的,浏览器的标准就是DOM 设计的非常复杂。当我们频繁的去做 DOM 更新,会产生一定的性能问题。
Virtual DOM 就是用一个原生的 JS 对象去描述一个 DOM 节点,所以它比创建一个 DOM 的代价要小很多。在 Vue.js 中,Virtual DOM 是用
VNode这么一个 Class 去描述
- 其实 VNode 是对真实 DOM 的一种抽象描述,它的核心定义无非就几个关键属性,标签名、数据、子节点、键值等,其它属性都是用来扩展 VNode 的灵活性以及实现一些特殊 feature 的。
- 由于 VNode 只是用来映射到真实 DOM 的渲染,不需要包含操作 DOM 的方法,因此它是非常轻量和简单的。
- Virtual DOM 除了它的数据结构的定义,映射到真实的 DOM 实际上要经历 VNode 的 create、diff、patch 等过程。
/* @flow */
export default class VNode {
tag: string | void;
data: VNodeData | void;
children: ?Array<VNode>;
text: string | void;
elm: Node | void;
ns: string | void;
context: Component | void; // rendered in this component's scope
key: string | number | void;
componentOptions: VNodeComponentOptions | void;
componentInstance: Component | void; // component instance
parent: VNode | void; // component placeholder node
// strictly internal
raw: boolean; // contains raw HTML? (server only)
isStatic: boolean; // hoisted static node
isRootInsert: boolean; // necessary for enter transition check
isComment: boolean; // empty comment placeholder?
isCloned: boolean; // is a cloned node?
isOnce: boolean; // is a v-once node?
asyncFactory: Function | void; // async component factory function
asyncMeta: Object | void;
isAsyncPlaceholder: boolean;
ssrContext: Object | void;
fnContext: Component | void; // real context vm for functional nodes
fnOptions: ?ComponentOptions; // for SSR caching
devtoolsMeta: ?Object; // used to store functional render context for devtools
fnScopeId: ?string; // functional scope id support
constructor (
tag?: string,
data?: VNodeData,
children?: ?Array<VNode>,
text?: string,
elm?: Node,
context?: Component,
componentOptions?: VNodeComponentOptions,
asyncFactory?: Function
) {
this.tag = tag
this.data = data
this.children = children
this.text = text
this.elm = elm
this.ns = undefined
this.context = context
this.fnContext = undefined
this.fnOptions = undefined
this.fnScopeId = undefined
this.key = data && data.key
this.componentOptions = componentOptions
this.componentInstance = undefined
this.parent = undefined
this.raw = false
this.isStatic = false
this.isRootInsert = true
this.isComment = false
this.isCloned = false
this.isOnce = false
this.asyncFactory = asyncFactory
this.asyncMeta = undefined
this.isAsyncPlaceholder = false
}
// DEPRECATED: alias for componentInstance for backwards compat.
/* istanbul ignore next */
get child (): Component | void {
return this.componentInstance
}
}
export const createEmptyVNode = (text: string = '') => {
const node = new VNode()
node.text = text
node.isComment = true
return node
}
export function createTextVNode (val: string | number) {
return new VNode(undefined, undefined, undefined, String(val))
}
// optimized shallow clone
// used for static nodes and slot nodes because they may be reused across
// multiple renders, cloning them avoids errors when DOM manipulations rely
// on their elm reference.
export function cloneVNode (vnode: VNode): VNode {
const cloned = new VNode(
vnode.tag,
vnode.data,
// #7975
// clone children array to avoid mutating original in case of cloning
// a child.
vnode.children && vnode.children.slice(),
vnode.text,
vnode.elm,
vnode.context,
vnode.componentOptions,
vnode.asyncFactory
)
cloned.ns = vnode.ns
cloned.isStatic = vnode.isStatic
cloned.key = vnode.key
cloned.isComment = vnode.isComment
cloned.fnContext = vnode.fnContext
cloned.fnOptions = vnode.fnOptions
cloned.fnScopeId = vnode.fnScopeId
cloned.asyncMeta = vnode.asyncMeta
cloned.isCloned = true
return cloned
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
用Vnode描述真实DOM
const elementVNode = {
tag: 'div',
data: null,
children: [
{
tag: 'h1',
data: null
},
{
tag: 'p',
data: null
}
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
不同的vnode拥有不同的设计,总体来说Vnode可以分为五类
- html/svg 元素、
- 组件、
- 纯文本、
- Fragment
- Portal**:

那么在 Vue.js 中,VNode 的 create 是通过之前提到的 createElement 方法创建的,我们接下来分析这部分的实现。
createElement
- vue.js 使用cerateElement方法创建Vnode
createElement方法实际上是对_createElement方法的封装,它允许传入的参数更加灵活,在处理这些参数后,调用真正创建 VNode 的函数_createElement:
// wrapper function for providing a more flexible interface
// without getting yelled at by flow
export function createElement (
context: Component,
tag: any,
data: any,
children: any,
normalizationType: any,
alwaysNormalize: boolean
): VNode | Array<VNode> {
if (Array.isArray(data) || isPrimitive(data)) {
normalizationType = children
children = data
data = undefined
}
if (isTrue(alwaysNormalize)) {
normalizationType = ALWAYS_NORMALIZE
}
return _createElement(context, tag, data, children, normalizationType)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
参数定义
context表示 VNode 的上下文环境,它是Component类型;tag表示标签,它可以是一个字符串,也可以是一个Componentdata表示 VNode 的数据,它是一个VNodeData类型,children表示当前 VNode 的子节点,它是任意类型的,它接下来需要被规范为标准的 VNode 数组;normalizationType表示子节点规范的类型,类型不同规范的方法也就不一样,它主要是参考render函数是编译生成的还是用户手写的。export function _createElement ( context: Component, tag?: string | Class<Component> | Function | Object, data?: VNodeData, children?: any, normalizationType?: number ): VNode | Array<VNode> { // ..... 省略 // support single function children as default scoped slot if (Array.isArray(children) && typeof children[0] === 'function' ) { data = data || {} data.scopedSlots = { default: children[0] } children.length = 0 } // children的规范化 if (normalizationType === ALWAYS_NORMALIZE) { children = normalizeChildren(children) } else if (normalizationType === SIMPLE_NORMALIZE) { children = simpleNormalizeChildren(children) } // Vnode的创建 let vnode, ns if (typeof tag === 'string') { let Ctor ns = (context.$vnode && context.$vnode.ns) || config.getTagNamespace(tag) if (config.isReservedTag(tag)) { // platform built-in elements vnode = new VNode( config.parsePlatformTagName(tag), data, children, undefined, undefined, context ) } else if (isDef(Ctor = resolveAsset(context.$options, 'components', tag))) { // component vnode = createComponent(Ctor, data, context, children, tag) } else { // unknown or unlisted namespaced elements // check at runtime because it may get assigned a namespace when its // parent normalizes children vnode = new VNode( tag, data, children, undefined, undefined, context ) } } else { // direct component options / constructor vnode = createComponent(tag, data, context, children) } if (Array.isArray(vnode)) { return vnode } else if (isDef(vnode)) { if (isDef(ns)) applyNS(vnode, ns) if (isDef(data)) registerDeepBindings(data) return vnode } else { return createEmptyVNode() } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
children的规范化
由于 Virtual DOM 实际上是一个树状结构,每一个 VNode 可能会有若干个子节点,这些子节点应该也是 VNode 的类型。_createElement 接收的第 4 个参数 children 是任意类型的,因此我们需要把它们规范成 VNode 类型。
simpleNormalizeChildren当functional component函数式组件返回的是一个数组而不是一个根节点的时候,通过Array.prototype.concat 将整个children数组打平,normalizeChildren方法的调用场景有 2 种- 一个场景是
render函数是用户手写的,当children只有一个节点的时候,Vue.js 从接口层面允许用户把children写成基础类型用来创建单个简单的文本节点,这种情况会调用createTextVNode创建一个文本节点的 VNode - 是当编译
slot、v-for的时候会产生嵌套数组的情况,会调用normalizeArrayChildren方法
- 一个场景是
// The template compiler attempts to minimize the need for normalization by
// statically analyzing the template at compile time.
//
// For plain HTML markup, normalization can be completely skipped because the
// generated render function is guaranteed to return Array<VNode>. There are
// two cases where extra normalization is needed:
// 1. When the children contains components - because a functional component
// may return an Array instead of a single root. In this case, just a simple
// normalization is needed - if any child is an Array, we flatten the whole
// thing with Array.prototype.concat. It is guaranteed to be only 1-level deep
// because functional components already normalize their own children.
export function simpleNormalizeChildren (children: any) {
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
if (Array.isArray(children[i])) {
return Array.prototype.concat.apply([], children)
}
}
return children
}
// 2. When the children contains constructs that always generated nested Arrays,
// e.g. <template>, <slot>, v-for, or when the children is provided by user
// with hand-written render functions / JSX. In such cases a full normalization
// is needed to cater to all possible types of children values.
export function normalizeChildren (children: any): ?Array<VNode> {
return isPrimitive(children)
? [createTextVNode(children)]
: Array.isArray(children)
? normalizeArrayChildren(children)
: undefined
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
normalizeArrayChildren 接收 2 个参数,
children表示要规范的子节点,nestedIndex表示嵌套的索引,
单个 child 可能是一个数组类型。 normalizeArrayChildren 主要的逻辑就是遍历 children,获得单个节点 c,然后对 c 的类型判断,
- 如果是一个数组类型,则递归调用
normalizeArrayChildren; - 如果是基础类型,则通过
createTextVNode方法转换成 VNode 类型;否则就已经是 VNode 类型了, - 如果
children是一个列表并且列表还存在嵌套的情况,则根据nestedIndex去更新它的 key。这里需要注意一点,在遍历的过程中,对这 3 种情况都做了如下处理:如果存在两个连续的text节点,会把它们合并成一个text节点。
经过对 children 的规范化,children 变成了一个类型为 VNode 的 Array。
Vnode的创建
对
tag做判断,如果是string类型,则接着判断如果是内置的一些节点,则直接创建一个普通 VNode,如果是为已注册的组件名,则通过
createComponent创建一个组件类型的 VNode,否则创建一个未知的标签的 VNode。如果是
tag一个Component类型,则直接调用createComponent创建一个组件类型的 VNode 节点。对于createComponent创建组件类型的 VNode 的过程,我们之后会去介绍,本质上它还是返回了一个 VNode。
// Vnode的创建
let vnode, ns
if (typeof tag === 'string') {
let Ctor
ns = (context.$vnode && context.$vnode.ns) || config.getTagNamespace(tag)
if (config.isReservedTag(tag)) {
// platform built-in elements
vnode = new VNode(
config.parsePlatformTagName(tag), data, children,
undefined, undefined, context
)
} else if (isDef(Ctor = resolveAsset(context.$options, 'components', tag))) {
// component
vnode = createComponent(Ctor, data, context, children, tag)
} else {
// unknown or unlisted namespaced elements
// check at runtime because it may get assigned a namespace when its
// parent normalizes children
vnode = new VNode(
tag, data, children,
undefined, undefined, context
)
}
} else {
// direct component options / constructor
vnode = createComponent(tag, data, context, children)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
update
Vue 的
_update是实例的一个私有方法,它被调用的时机有 2 个,一个是首次渲染,一个是数据更新的时候
Vue.prototype._update = function (vnode: VNode, hydrating?: boolean) {
const vm: Component = this
const prevEl = vm.$el
const prevVnode = vm._vnode
const prevActiveInstance = activeInstance
activeInstance = vm
vm._vnode = vnode
// Vue.prototype.__patch__ is injected in entry points
// based on the rendering backend used.
if (!prevVnode) {
// initial render
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(vm.$el, vnode, hydrating, false /* removeOnly */)
} else {
// updates
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(prevVnode, vnode)
}
activeInstance = prevActiveInstance
// update __vue__ reference
if (prevEl) {
prevEl.__vue__ = null
}
if (vm.$el) {
vm.$el.__vue__ = vm
}
// if parent is an HOC, update its $el as well
if (vm.$vnode && vm.$parent && vm.$vnode === vm.$parent._vnode) {
vm.$parent.$el = vm.$el
}
// updated hook is called by the scheduler to ensure that children are
// updated in a parent's updated hook.
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
因为在服务端渲染中,没有真实的浏览器 DOM 环境,所以不需要把 VNode 最终转换成 DOM,因此是一个空函数
Vue.prototype.__patch__ = inBrowser ? patch : noop
import * as nodeOps from 'web/runtime/node-ops'
import { createPatchFunction } from 'core/vdom/patch'
import baseModules from 'core/vdom/modules/index'
import platformModules from 'web/runtime/modules/index'
// the directive module should be applied last, after all
// built-in modules have been applied.
const modules = platformModules.concat(baseModules)
export const patch: Function = createPatchFunction({ nodeOps, modules })
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
const hooks = ['create', 'activate', 'update', 'remove', 'destroy']
export function createPatchFunction (backend) {
let i, j
const cbs = {}
const { modules, nodeOps } = backend
for (i = 0; i < hooks.length; ++i) {
cbs[hooks[i]] = []
for (j = 0; j < modules.length; ++j) {
if (isDef(modules[j][hooks[i]])) {
cbs[hooks[i]].push(modules[j][hooks[i]])
}
}
}
return function patch(oldVnode, vnode, hydrating, removeOnly){
// ....
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
总结
vue内遍历子虚拟节点,递归调用 createElm,这是一种常用的深度优先的遍历算法,这里要注意的一点是在遍历过程中会把 vnode.elm 作为父容器的 DOM 节点占位符传入。实际上整个过程就是递归创建了一个完整的 DOM 树并插入到 Body 上。
初始化vue到最终渲染的整个过程
← 生命周期 Vue.js技术揭秘大纲→